Describe the Two Major Types of Active Transport.
The outer layer is made up of the. The second transport method is still considered active because it depends on the use of energy as does primary transport Figure 3.
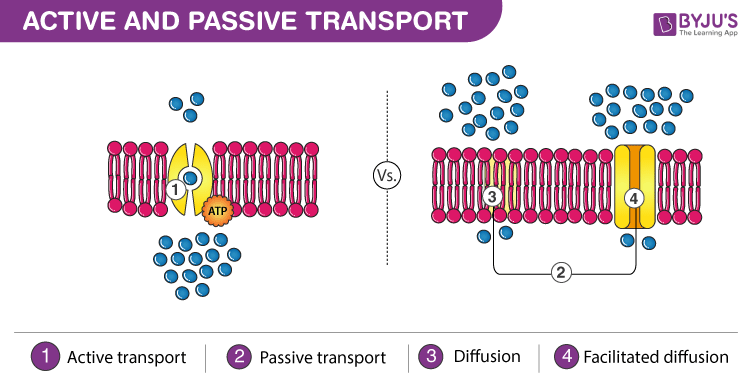
Difference Between Active Transport And Passive Transport
There are four main types of passive transport.

. Passive transport which includes Simple Diffusion Osmosis Facilitated Diffusion Active Transport may involve a pump or a gallbladder pump Transport may be Vesicles Transport may involve Endocytosis. Cellular transport can be classified as follows. Two K and three Na are transported through the membrane for each molecule of ATP dephosphorylated.
Introduction Passive transport is a great strategy for moving molecules into or out of a cell. Primary and secondary active transport. Active and passive transport processes are two ways molecules and other materials move in and out of cells and across intracellular membranes.
There are two types of active transport. Active transport pumps molecules or substances against a concentration gradient using cellular energy. There are two types of Active transport.
ENE2 EU ENE2G LO ENE2G2 EK ENE2G3 EK ENE2G4 EK Electrochemical gradients and the membrane potential. Endocytosis is the process of taking material into the cell by means of pockets throughout the cell. Calcium ions moving from cardiac muscle cells.
There are three main types of Active Transport. Primary Active transport Secondary Active transport Exocytosis endocytosis and sodium-potassium pump are a few examples of active transport. Here are some examples of active transport in animals and humans.
The main aim of both the transport system is to carry molecules and ions across the cellular membrane. Transport of Na and K through the plasma membrane is believed to occur in the following stages see Fig. Active Transport requires energy ATP- movement of material against their concentration gradient from areas of lower concentration to areas of high concentration.
A macrophage ingesting a bacterial cell. The main difference between primary and secondary active transport is the source of energy used by each transport method in order to transport molecules across the cell membrane. Up to 24 cash back Active Transport Active Transport is the term used to describe the processes of moving materials through the cell membrane that requires the use of energy.
Endocytosis Cells ingest substances. Sodium-potassium pump exchange of sodium and potassium ions across cell walls Amino acids moving along the human intestinal tract. Exocytosis is the process through which many cells release a large amount of material.
The Sodium-Potassium pump Exocytosis and Endocytosis. Primary Active Transport Active transport of small molecules that directly uses ATP as an energy source Secondary Active Transport Active transport. The main three types of active transport are.
Primary and secondary active transport are the two variations of active transport of molecules across biological membranes. The two major types of active transport are endocytosis and exocytosis. The two major types of active transport are endocytosis and exocytosis.
Exocytosis is the process through which many cells release a large amount of material. The two major types of active transport are endocytosis and exocytosis. Describe the two major types of active transport.
Active transport is the movement of molecules or ions against a concentration gradient from an area of lower to higher concentration which does not ordinarily occur so enzymes and energy are required. These cells transport nutrients chemicals and other substances to other cells by using this vital transport system. The process of endocytosis and exocytosis are utilized by all the cells for transportation of molecules which cannot passively permeate via the membrane.
In primary active transport specialized trans-membrane proteins recognize the presence of a substance that needs to be transported and serve as pumps powered by the chemical energy ATP to carry the desired biochemicals across. Active and passive transport are the two systems of transporting molecules across the cell membrane. Exocytosis Processes of releasing contents of the cell to the external environment.
Glucose moving in or out of a cell. Primary Active Transport The primary active transport that functions with the active transport of sodium and potassium allows secondary active transport to occur. Exocytosis is the process through which many cells release a large amount of material.
Lastly active transport can be accomplished through processes called endocytosis and exocytosis. Endocytosis is the process of taking material into the cell by means of pockets throughout the cell. Three sodium ions and one molecule of ATP inside the cell are bound to specific sites on the enzyme carrier while two potassium ions are bound to a.
Describe the two major types of active transport. Endocytosis is the process of taking material into the cell by means of pockets throughout the cell. Furthermore what are the different.
In exocytosis a cell moves something outside of itself in large quantities by wrapping it in a membrane called a vesicle and spitting out the vesicle. In primary active transport ATP is used in form of the energy. This transport mechanism present in the body is of two types like active and passive.
3 6 Active Transport Concepts Of Biology 1st Canadian Edition
Difference Between Primary And Secondary Active Transport Definition Types Characteristics Similarities Differences


No comments for "Describe the Two Major Types of Active Transport."
Post a Comment